Seismic Facies Analysis
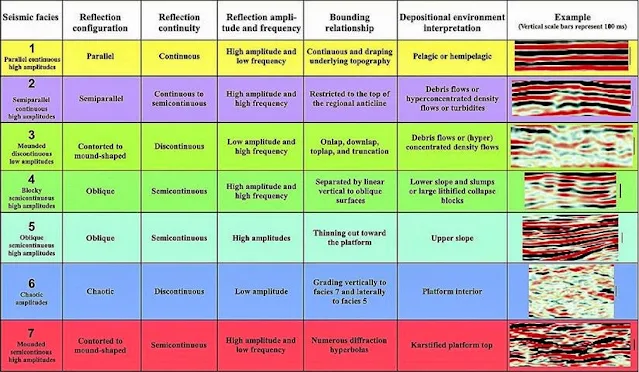
Seismic facies are "mappable, three dimensional seismic units composed of groups of reflections whose parameters differ from those of adjacent facies units”.
Seismic facies analysis is the description and interpretation of seismic reflection parameters, such as configuration, continuity, amplitude, and frequency, within the stratigraphic framework of a depositional sequence.
Its purpose is to determine all variations of seismic parameters within third-order sequences and their systems tracts in order to determine lateral lithofacies and fluid type changes. Of these parameters, reflection pattern geometries are perhaps the most useful for calibration with lithofacies interpreted from well logs, cores, and cuttings.
Reflection parameters
Depositional environment, sediment source, and lithofacies can be interpreted by grouping these parameters into mappable, three-dimensional seismic facies.The table below summarizes the information obtained from each parameter.
- Seismic forward modeling
- Changing display scale for seismic data
- Changing display type for seismic data
- Using 3-D seismic displays
Seismic facies mapping
- Identify sequences that contain potential traps, seal rocks, reservoir rocks, or source rocks.
- Make regional seismic reflection pattern maps and isochron maps of those sequences. If possible, make maps of lowstand, transgressive, and highstand systems tracts.

